M-Close Kit
Over 127 peer reviewed studies show significant benefits from abdominal wall blocks.
- 67% reduction in post-op opiate use vs local infiltration 5
- Over 70% of patients report being pain free at 1 hour after laparoscopic surgery 6
- Abdominal blocks tripled the time to first rescue analgesia 7
- Patients were discharged significantly earlier 8
- Rectus Sheath Blocks can provide sufficient pain control without the need for any other post-op analgesia 1
Watch the video below to see how a targeted nerve block can be administered as well as laparoscopic port site closed in 45 seconds (BMI=43)!
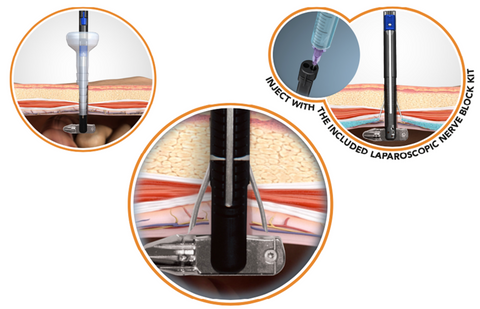
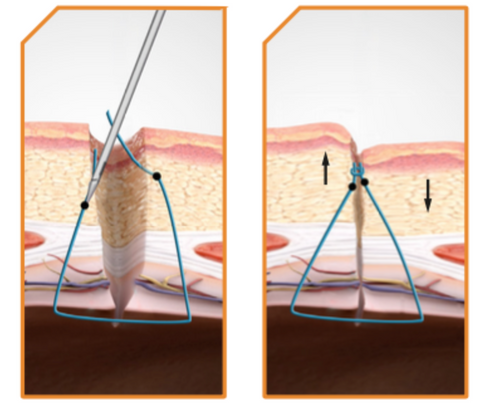
M-CLOSE USES A PATENTED REFERENCE PLANE SYSTEM, WHICH POSITIONS THE NERVE BLOCK NEEDLE RELATIVE TO THE PERITONEUM, NOT THE SKIN SURFACE.
M-CLOSE PROVIDES A GOLD STANDARD CLOSURE
- Adheres to the Jonsson-Israelsson rules of fascial closure
- Suture bites are symmetrical and 1cm from each side of the defect
- Knot is above the fascial plane
M-CLOSE IS SAFE
- No exposed needles help prevent sharps injuries
- Shielded needles can help prevent injury to intra-abdominal organs, even without pneumoperitoneum, or direct visualization 13
M-CLOSE IS EASY
- <30 seconds to place the suture
- Deploys two needles at once
- Can place multiple sutures for large defects
M-CLOSE KIT SAVES MONEY
- Costs less than most port closure devices
- Reduce costs related to post-op port site complications
- Save O.R. time by closing ports faster and avoiding unnecessary scope exchanges
- Deliver targeted anaesthesia at no extra cost
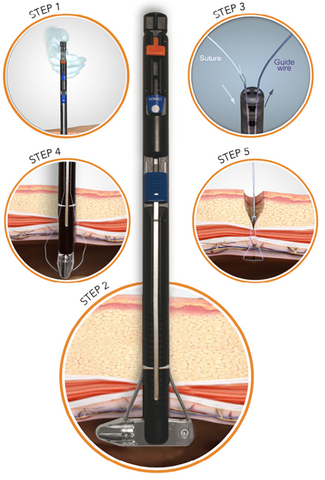
M-CLOSE KIT IS EASY TO USE
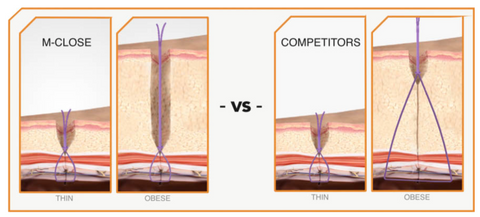
M-CLOSE IS DESIGNED FOR OBESE PATIENTS
M-Close uses the fascia as a reference to produce suture loops that are always the SAME SIZE, regardless of abdominal wall thickness.
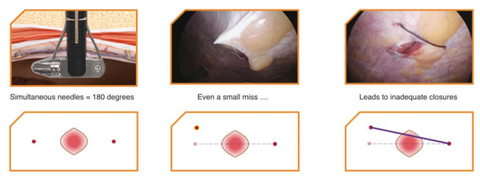
M-Close Kit simultaneously deploys two opposing needles, ensuring proper 180 degree placement every time.

M-Close Kit simultaneous symmetrical needles always enter at the same height to reduce or eliminate dimpling.

How to use M-Close Kit
Downloads
Estape Study: Preliminary findings from a study of 217 Patients
Available in New Zealand.
CONTACT US FOR MORE INFORMATION
Contact us at info@mangomedtech.co.nz
References:
- Willschke, H et al. Ultrasonography-guided rectus sheath block in pediatric anesthesia: a new approach to an old technique. Br J Anesthesia. 2006; 97(2): 244-249
- Salinas, FV. Ultrasound-guided rectus sheath block: Clinical Anatomy. Philips tutorial. 2015
- Based on internal report: Ultrasound Analysis of the Rectus Sheath in 93 subjects. Sept. 2018
- Kim, J. Thickness of Rectus Abdominis Muscle and Abdominal Subcutaneous Fat Tissue in Adult Women: Correlation with Age, Pregnancy, Laparotomy, and Body Mass Index. Archives of Plastic Surgery 2012; 39(5)
- Crosbie, EJ et al. The surgical rectus sheath block for post-operative analgesia: a modern approach to an established technique. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology. 2012; 160: 196–200
- Dingeman, RS et al. Ultrasonography-Guided Bilateral Rectus Sheath Block vs Local Anesthetic Infiltration After Pediatric Umbilical Hernia Repair A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Surg. 2013 Aug; 148(8): 707-13
- Shah, VA et al. Ultrasound guided abdominal field blocks improve postoperative pain relief in cesarean delivery: a prospective randomized controlled study. Anesthesia Pain and Intensive Care. 2017; Vol 21(2): 218-223
- Smith, BE et al. Rectus sheath and mesosalpinx block for laparoscopic sterilization. Anesthesia. 1991; 46: 875-877
- Chazapis, M et al. Improving the Peri-operative care of Patients by instituting a 'Block Room' for Regional Anaesthesia. BMJ Quality Improvement Reports 2014
- McDermott, G et al. Should we stop doing blind transversus abdominis plane blocks? Br J Anesthesia 2012: 108 (3): 499–502
- As described in US Patent # 9,451,950 Β2
- Working Port-Site Hernias: To Close or Not to Close? Does It Matter in the Obese? Bariatric Times June 7, 2011
- Based on internal report: M-Close performance testing, July 2018
- Owens, M. A systematic review of laparoscopic port site hernias in gastrointestinal surgery. Surgeon 2011 Aug; 9(4): 218-24.
- Smith BE, Suchak M, Siggins D, Challands J. Rectus sheath block for diagnostic laparoscopy. Anaesthesia. 1988;43:947–8.
